Feeling the Strain of Data Security Concerns in Your Business?
In today’s digital world, protecting sensitive information is paramount. Traditional methods can be cumbersome and leave vulnerabilities. But what if there was a technology that offered enhanced security, data privacy, and streamlined operations?
This is where private blockchain networks come in. Let’s delve deeper and explore how these innovative networks can revolutionize your business.
Transforming Business with Secure Networks

Source: Freepik
The world of business is constantly evolving, and new technologies are emerging to address the challenges of an increasingly digital landscape. One such technology with immense potential is blockchain. At its core, blockchain is a revolutionary system for recording information in a way that is distributed, secure, and tamper-proof. This is achieved through a concept called a distributed ledger, where data is not stored on a single server but replicated across a network of computers. Each record, or “block,” in this ledger is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating an immutable chain of transactions. Any attempt to alter a record would be immediately detectable, ensuring the integrity and security of the data.
However, the world of blockchain isn’t one-size-fits-all. We have two main types: private and public blockchains. Public blockchains, like those used for popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, are open to anyone to participate. While they offer a high degree of transparency, they may not be ideal for businesses due to concerns about data privacy and scalability.
This is where private blockchains come in. Unlike their public counterparts, private blockchains are permissioned networks, meaning only authorized participants can access and contribute data. This restricted access model offers businesses several advantages, including:
- Enhanced Security: By limiting access, private blockchain networks significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized modifications or breaches.
- Increased Data Privacy: Sensitive business information remains confidential within the private blockchain network, fostering trust and compliance with data protection regulations.
- Improved Control: Businesses have greater control over who can join the network and what data is shared, allowing for a more streamlined and efficient operation.
The growing interest in private blockchain technologies reflects their potential to transform various aspects of business. From supply chain management to financial transactions, these secure and controlled access networks offer a powerful tool for businesses to enhance security, privacy, and overall efficiency. As we delve deeper into this guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of private blockchain networks, their functionalities, and how they can empower businesses to operate with greater confidence and control in today’s digital age.
Public vs. Private Blockchains: Tailoring Security for Your Needs
Public blockchains, like Bitcoin, have revolutionized secure transactions for digital currencies. But what if your business needs a more controlled environment for sensitive data, specific to your organization or a trusted group of partners? This is where private blockchain technology, also known as permissioned blockchains, come into play.

Source: Freepik
Demystifying Private Blockchain Networks:
Think of public blockchains as an open marketplace – anyone can join and participate. Private blockchain networks, on the other hand, function more like a private club with a shared ledger. Here, access is restricted to a select group of authorized users, typically managed by a central authority. This control over who can join and interact with the network offers significant advantages, particularly for industries like healthcare that handle highly sensitive data.
Enhanced Security and Privacy for Electronic Health Records (EHRs):
Private blockchain technology excels at safeguarding sensitive information. By limiting access points, they significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. This controlled environment is ideal for managing Electronic Health Records (EHRs).
Imagine a secure network where only authorized healthcare providers, with a patient’s consent, can access their complete medical history. This fosters trust and facilitates better care coordination. Additionally, patients gain more control over their EHR data, allowing them to selectively share it with different providers as needed. Private blockchain technology empowers healthcare institutions to comply with data protection regulations by ensuring stricter control over who sees the data and how it’s used.
This focus on security and privacy extends beyond healthcare. Private blockchain networks offer similar benefits for various industries where sensitive business information needs protection.
Validating Transactions in a Controlled Network:
Public blockchains rely on complex consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) to validate transactions. In private blockchain nerworks, different mechanisms can be used, depending on the specific needs of the network. One common approach is Proof of Authority (PoA). Here, pre-selected, trusted entities (e.g., companies or organizations) act as validators, verifying the legitimacy of transactions. This approach is faster and more energy-efficient compared to PoW, making it suitable for private networks with a smaller, well-defined group of participants.
The next section will delve into the key benefits of a private blockchain for businesses, exploring how these secure and permissioned networks can unlock real-world value.
Transforming Financial Services with Private Blockchain
Financial institutions are constantly seeking innovative solutions to improve efficiency, security, and transparency in their operations. Private blockchain networks, a revolutionary technology built on the foundation of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), are emerging as a game-changer in this domain.
Unveiling the Power of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT):
At its core, DLT allows for the creation of a secure and transparent shared ledger. Imagine a digital record of transactions, accessible to authorized participants (banks, institutions) but not publicly available. This shared ledger eliminates the need for centralized record-keeping, fostering trust and collaboration within the network.
Faster Transactions, Streamlined Processes:
Traditional financial transactions can be slow and cumbersome, often involving multiple intermediaries and manual processes. Private blockchains eliminate these inefficiencies. By streamlining data exchange and validation through secure consensus mechanisms, private blockchains significantly accelerate transaction processing times.
Enhanced Security Through Data Encryption:
Financial data is highly sensitive, and its protection is paramount. Private blockchain networks address this concern by employing robust data encryption techniques. Only authorized participants have access to the data, and even then, it remains encrypted, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of financial information.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): Ensuring Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is crucial for any financial system. Private blockchain networks leverage consensus mechanisms like PBFT to guarantee that all participants agree on the state of the ledger. PBFT ensures that even if a node malfunctions or attempts to tamper with data, the network remains secure, and the correct information prevails.
Secure Sharing of Private Data: Collaboration with Confidence
Private blockchains excel at facilitating the secure sharing of sensitive financial data among authorized institutions. This enables collaboration on projects, regulatory compliance processes, and fraud prevention initiatives, all within a secure and controlled environment.
Streamlining Cross-Border Payments: A Global Opportunity
Cross-border payments are often plagued by delays and high fees. Private blockchains provide a promising solution. By enabling faster and more efficient transfer of funds across borders, private networks have the potential to revolutionize the global financial landscape.
By leveraging these advantages of private blockchain technology, financial institutions can unlock a new era of efficiency, security, and collaboration within the financial services industry.
Building Your Private Blockchain Network: Options and Considerations
The potential benefits of private blockchain technology are undeniable, but navigating the technical aspects of implementation can be daunting. Here’s a breakdown of different approaches to consider:
1. Types of Private Blockchains:
- Standalone Private Blockchains: These permissioned networks are designed and controlled by a single financial institution for internal use. They offer the highest degree of control and customization over the network. However, developing and maintaining a standalone private blockchain requires significant technical expertise and resources, making it a suitable option primarily for large institutions.
- Niche Private Blockchains (or Consortium Blockchains): These permissioned networks involve multiple financial institutions collaborating to manage the blockchain. This structure fosters trust and collaboration within a specific industry segment, allowing institutions to share resources and expertise while maintaining control over sensitive data.
2. Implementation Strategies:
- Building from Scratch: While technically possible, building a private blockchain solution from scratch requires significant technical expertise and resources. This approach might be suitable for large enterprises with the in-house capabilities to handle complex development processes.
Alternative Options for Leveraging Private Blockchains:
Fortunately, businesses have several other options for leveraging your private blockchain, avoiding the complexities of building from scratch:
- Existing Private Blockchain Platforms: Several open-source and permissioned blockchain platforms are readily available, such as Hyperledger Fabric and Quorum. These platforms offer pre-built frameworks and tools, enabling faster development and deployment of a private blockchain. This approach reduces development time and costs compared to building from scratch.
- Partnering with Blockchain Technology Providers: Businesses can also leverage the expertise of established blockchain technology providers. These providers offer a range of services, including custom development, integration with existing systems, and ongoing maintenance and support. Partnering with a provider allows businesses to benefit from the expertise of specialists without the need for in-house blockchain development capabilities.
By carefully considering the type of private blockchain network and the most suitable implementation strategy, financial institutions can unlock the transformative potential of this technology and gain a competitive edge in the evolving financial landscape.
The Cost of Private Blockchains: A Balancing Act
The cost of implementing a private blockchain solution can vary significantly depending on several factors:
- Platform Choice: Open-source platforms like Hyperledger Fabric are generally free to use, while proprietary solutions may require licensing fees.
- Development Complexity: Building a niche, highly customized solution will naturally be more expensive than deploying a general-purpose platform.
- Network Size: The number of participants and the required level of decentralization can impact costs. Typically, networks with fewer nodes are more cost-effective.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Maintaining the network and ensuring its security requires ongoing resources. Factor in the cost of ongoing support when making your decision.
The key takeaway is that the cost of a private blockchain solution should be viewed as an investment. While upfront costs can be significant, the potential for enhanced security, improved efficiency, and streamlined collaboration can lead to substantial long-term benefits for businesses.
Public vs. Private Blockchains: Understanding the Key Differences
While both public and private blockchains share the core principles of distributed ledgers and immutability, they cater to distinct needs. Here’s a clear comparison to help you understand the key differences:
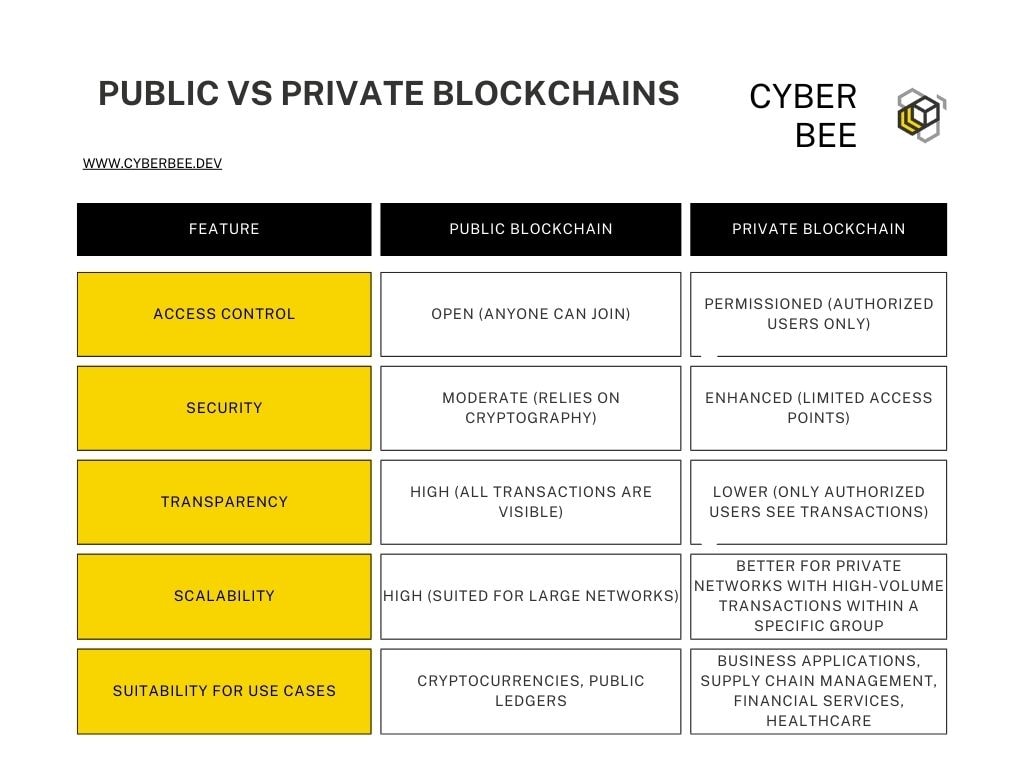
Let’s break down these key differences:
- Access Control: Public blockchains function like open networks, where anyone can join and participate in the consensus process. Private blockchains, on the other hand, operate on a permissioned basis. A central authority manages access and determines who can join the network.
- Security: Public blockchains rely on complex cryptography and distributed consensus mechanisms to secure the network. While secure, they can be vulnerable to attacks if a significant amount of computing power is concentrated in malicious hands (51% attack). Private blockchains, with their limited access points, offer a more secure environment for handling sensitive business data.
- Transparency: Public blockchains provide complete transparency, as all transactions are publicly viewable on the blockchain. This transparency can be essential for building trust in cryptocurrencies. However, for businesses dealing with confidential information, the lack of privacy in public blockchains can be a drawback. Private blockchains offer a more controlled level of transparency, allowing authorized participants to view relevant transactions while maintaining data privacy.
- Scalability: Public blockchains, with their large and decentralized nature, can experience scalability challenges as the number of transactions increases. Private blockchains, with their smaller, permissioned networks, are generally better suited for handling high-volume transactions within a specific group of participants.
- Use Cases: Public blockchains are the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. They also serve as public ledgers for recording and tracking various types of data. Private blockchains, on the other hand, are ideal for business applications where security, privacy, and control over data are paramount. They are transforming industries like supply chain management, finance, and healthcare by enabling secure collaboration and streamlining data exchange between trusted partners.
Additional Considerations for Private Blockchain Networks
While private blockchains offer significant advantages, some key considerations need to be addressed:
- Scalability for Future Growth: While private blockchain technology can handle high-volume transactions within a specific group, scaling them for significant future growth may require additional development. Researching scalability solutions like sharding, a technique that partitions the blockchain into smaller segments, is crucial for long-term planning.
- Data Integrity and Regulatory Compliance: Since private blockchains can be permissioned, it’s essential to ensure the integrity of data entered into the network. This may involve establishing clear data governance policies and procedures to maintain data accuracy and reliability. Additionally, compliance with relevant industry regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare data, needs to be carefully considered when designing and implementing private blockchains.
Transforming Businesses with Blockchain Technology
At Cyber Bee, we’re experts in unlocking the power of blockchain technology for businesses. Whether you need a secure environment for private data (like medical records) or faster transactions (in supply chains), we can deliver. Here’s how blockchain can revolutionize your industry:
Private Blockchains:
- Secure & Permissioned: Grant access only to authorized users, ideal for consortium blockchains where multiple organizations collaborate (e.g., banks in trade finance).
- Enhanced Privacy: Selective disclosure (zero-knowledge proofs) protects confidential data (e.g., patient health records) while maintaining transparency.
- Faster Processing: Compared to traditional systems, smart contracts automate tasks and streamline processes, leading to faster transactions.
- Control & Governance: Organizations have more control over the network’s rules and regulations compared to public blockchains.
Public Blockchains:
- Transparency & Decentralization: All participants have access to the shared ledger, fostering trust and reducing reliance on centralized entities.
- Security & Immutability: Cryptographic hashes and consensus mechanisms ensure data security and prevent unauthorized modifications.
- Scalability & Openness: Public blockchains can handle a high volume of transactions and are open to anyone to participate (unlike private blockchains).
Our Expertise:
We deliver innovative solutions across both private and public blockchains.
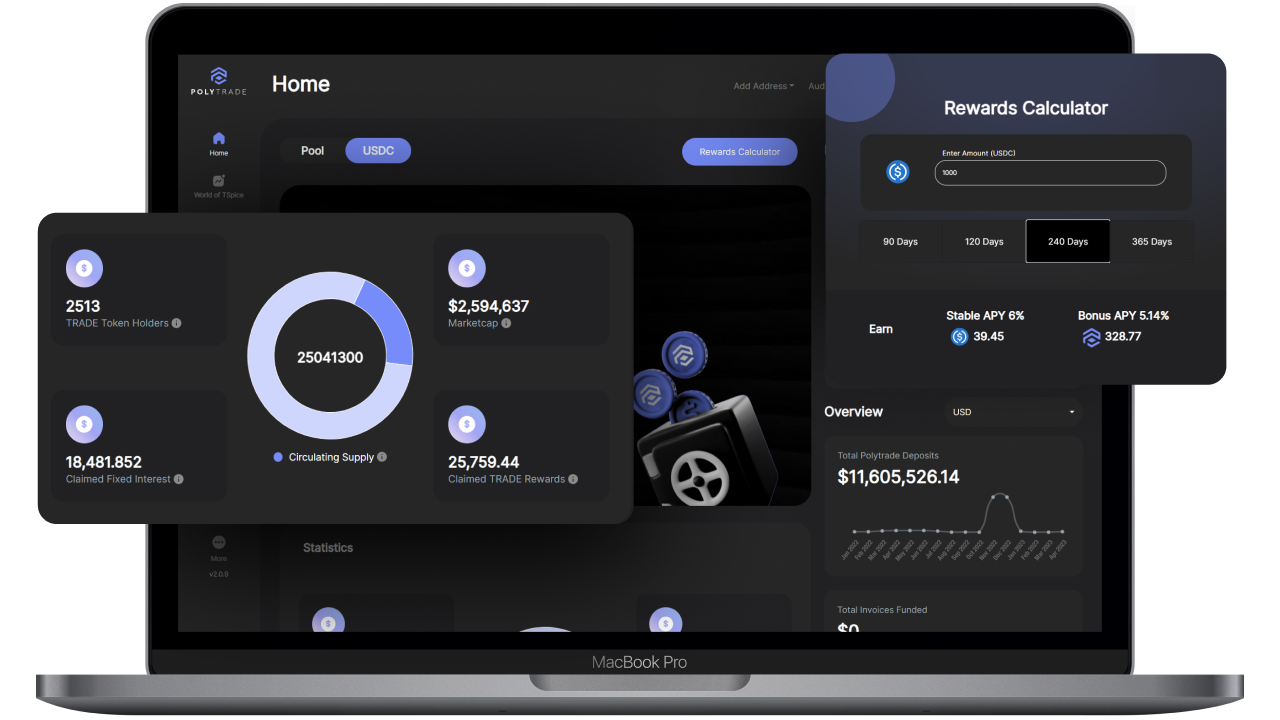
- Private Blockchain Example: Polytrade This platform uses a private blockchain to streamline trade finance for SMEs. It tackles slow payment times by enabling them to sell invoices for immediate payment.
- Public Blockchain Example: High-Speed Layer-1 Platform Our team developed a high-speed public blockchain that can process thousands of transactions per second, overcoming limitations of existing platforms.
Let’s discuss how blockchain technology can benefit your organization. We can help you choose the right type of blockchain (private, public, or consortium) based on your specific needs.
Conclusion
These two case studies offer a compelling glimpse into how Cyber Bee is helping businesses unlock the transformative potential of both private and public types of blockchain technologies. Whether you’re interested in a secure private network for data management or a high-speed public network for efficient transactions, our team has the expertise to deliver innovative solutions tailored to your specific needs. We invite you to explore our portfolio and contact us to discuss how blockchain technology can benefit your organization.



