Role of AI in Cyber Defense
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity is a critical concern for organizations of all sizes. The utilization of Artificial Intelligence in the realm of cybersecurity has become a cornerstone for developing advanced defense mechanisms against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. AI’s value in cybersecurity stems from its unparalleled ability to process vast datasets at speeds unmatchable by human counterparts, coupled with its ability to learn and adapt over time.
AI-driven cybersecurity tools offer the capability to continuously learn from the data they process, allowing them to identify new patterns that could indicate hacks. As cybercriminals evolve their tactics, AI tools similarly advance, effectively keeping pace with the latest methods of attack. The dynamic nature of AI means that these systems can become more accurate and effective the more they are used, creating a constantly improving security posture.
This adaptive strength is particularly important when it comes to defending against zero-day attacks—newly discovered vulnerabilities for which there is no known fix. AI systems can potentially identify and mitigate such vulnerabilities in real-time, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit them. In essence, AI in cybersecurity isn’t just an added layer of protection; it’s a proactive, evolving guardian that enhances an organization’s ability to defend against and respond to cyber threats efficiently and effectively.
Current Challenges in the Cybersecurity Industry
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, presenting numerous challenges for organizations. One of the primary challenges is the rapid increase in the volume and sophistication of cyber threats. Hackers are continually developing new methods to breach defenses, often outpacing traditional security measures.
Another significant challenge is the sheer volume of data that needs to be monitored and analyzed for potential threats. With the expansion of IoT and the increasing interconnectedness of devices, the attack surface has grown exponentially, making it more difficult to secure.
Additionally, there is a global shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, which leaves many organizations vulnerable and under-resourced in their defense efforts. The rise of complex regulatory requirements across different regions further complicates the security landscape, demanding more nuanced and compliant security measures.
How AI-based Approaches to Cybersecurity Differ from Traditional Approaches
AI-based approaches to cybersecurity mark a significant departure from traditional methods. Traditional cybersecurity relies heavily on signature-based detection methods, which require prior knowledge of attack patterns. This approach is less effective against zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats that do not match known signatures.
In contrast, AI-driven cybersecurity utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze patterns and anomalies in data, enabling the detection of threats without prior knowledge of their specific signatures. AI systems can process and analyze data at a scale and speed unattainable by human analysts, making them more efficient in identifying potential threats.
Furthermore, AI’s ability to learn and adapt over time means that these systems continually improve their accuracy, becoming more adept at predicting and mitigating future threats. This adaptive capability allows AI-driven cybersecurity to stay ahead of the evolving tactics of cybercriminals, offering a more dynamic and proactive approach to digital defense.
Technical Underpinnings
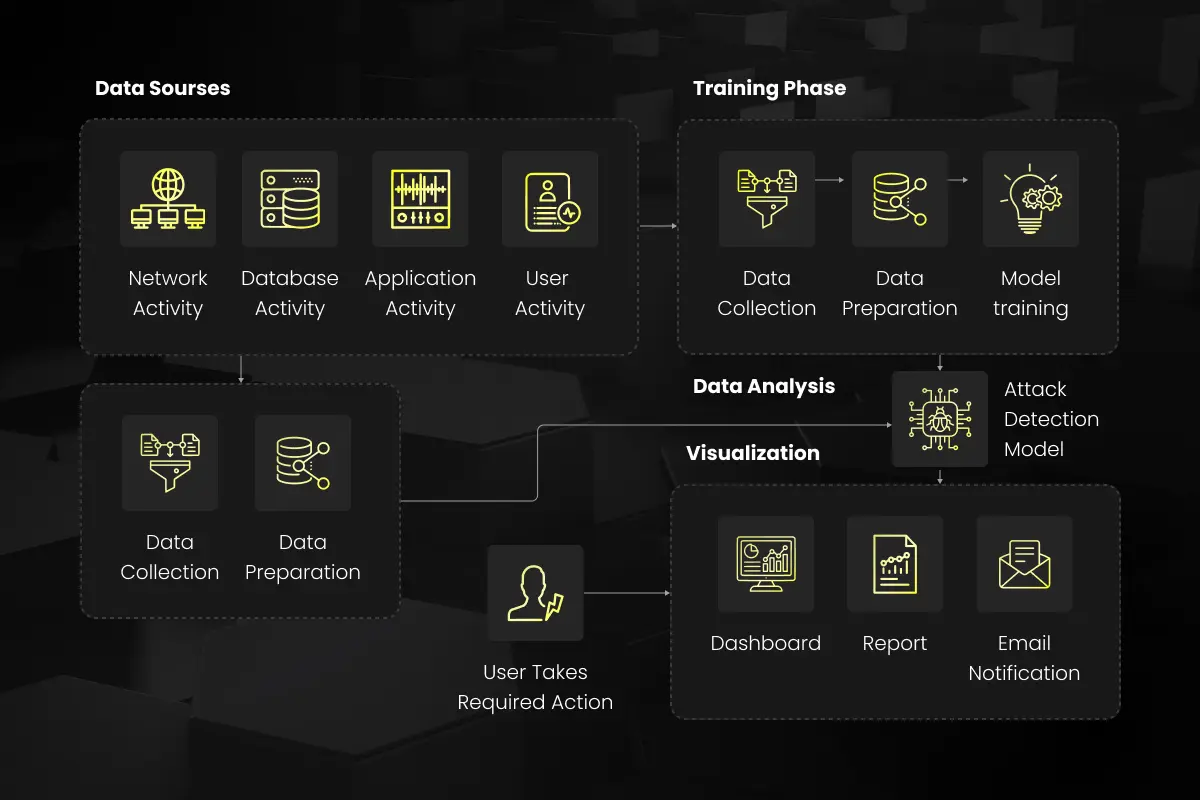
At the heart of AI-enabled cybersecurity is the transformation of data into protection. This process begins with the accumulation of extensive security-related data from across an organization’s digital infrastructure. This includes network traffic, login attempts, and normal user behavior patterns, to name a few. The collected data must be both comprehensive and granular to provide a solid foundation for the next steps.
Once the data pool is established, the raw data is then refined through a series of preprocessing steps. These steps may involve normalization, where data is scaled to a small, specified range; encoding, where categorical data is transformed into a numerical format; or feature selection, where only the most relevant data attributes are retained for model training.
Following the data preparation, an AI model is chosen and trained using the cleaned dataset. The selection of the model—be it a neural network for deep learning or a more traditional machine learning algorithm like decision trees or support vector machines—is dependent on the specific characteristics of the cybersecurity task at hand. Each model type has its own set of strengths; some may be better at detecting anomalies, while others might excel at classifying types of behavior as benign or malicious.
In the training phase, the model is exposed to both normal operations and known attack vectors to learn what constitutes a threat. This learning process is not static; it involves a feedback loop where the model’s performance is continuously assessed and improved upon. Over time, the model’s accuracy is enhanced as it encounters new data and potential threats.
The operational phase involves deploying the trained model into the active environment where it begins real-time analysis and monitoring. As new data flows in, the AI model assesses it against the patterns it has learned, looking for discrepancies that may signal a breach or an emerging threat. When a potential threat is identified, an alert is generated, and depending on the system’s sophistication, the AI can either recommend an action or autonomously implement a defensive response.
The true strength of AI in cybersecurity lies in its ongoing evolution. AI systems are designed to adapt and learn from each new attack, making them increasingly adept at predicting and mitigating future threats. This results in a cybersecurity posture that is proactive, resilient, and continuously improving, an essential feature in the fight against ever-evolving cyber threats.
Use Cases: From Detection to Prediction

- Spam Filtering
Spam filters have long been the first line of defense in protecting users from unwanted email and potential phishing attacks. AI enhances traditional spam filtering by learning from patterns of behavior and content. It doesn’t just rely on known spam signatures or blacklisted IP addresses; it intelligently examines the context, language, and even image content to understand and predict new spam tactics, thus keeping inboxes cleaner and more secure. - Malware Detection
Traditional antivirus software relies heavily on signature-based methods that can struggle to keep up with the tens of thousands of new malware variants created daily. AI steps in as a dynamic protector. By analyzing the attributes of files and their behavior within the system, AI can detect and quarantine even previously unknown malware types, all in real-time, effectively shrinking the window of vulnerability and enhancing system security. - Network Security
AI systems enhance network security by learning to detect unusual patterns that could indicate a breach, such as strange login locations or times, unusual data flows, or spikes in traffic. By continuously monitoring network behavior, AI systems can alert teams to potential threats faster than humanly possible, facilitating quicker response times and potentially preventing breaches before they occur. - Security Log Analysis
Security teams often face the challenge of sifting through millions of logs to identify potential threats, a task that is not only time-consuming but also prone to human error. AI significantly augments this process through automated log analysis, correlating disparate data and highlighting unusual activities without human intervention. This capability ensures that even the most subtle hints of a security threat are identified and flagged for investigation. - Phishing Detection
Phishing attempts have grown increasingly sophisticated, often bypassing traditional detection methods. AI models trained in linguistic analysis can scrutinize emails for phishing indicators, including nuanced textual cues and meta-data anomalies. Moreover, AI-driven systems extend their vigilance to observe user interactions, identifying actions like engaging with dubious links or entering sensitive details following a deceptive email. Such activities, when detected, trigger an immediate alert to security personnel, thereby enhancing the responsiveness of the cyber defense strategy.
Final thoughts
In summary, AI is not just a tool but a game-changer in cybersecurity. Its adoption is no longer a luxury but a necessity for those who wish to navigate the complexities of modern cyber threats. At Cyber Bee, we harness the power of AI to safeguard your digital environment. With our state-of-the-art AI solutions, we offer proactive threat detection, real-time security insights, and strategic defense mechanisms that adapt to the evolving threat landscape.
We invite you to explore how our AI-driven cybersecurity services can fortify your organization’s defenses. Contact us to learn more about our offerings and how we can tailor a cybersecurity strategy that meets your unique challenges. Let us empower you with AI, ensuring your peace of mind in the digital age.



